Background:
Concrete is one of the most widely used materials on the planet. It serves as the foundation of the construction industry. The global production of concrete is estimated to be 23 billion tons per year. When compared to other materials, concrete has the highest greenhouse gas emissions per unit mass, posing a climate risk. Furthermore, the waste generated as a result of the processes that produce its ingredients may pose a significant threat to the environment and hydraulic structures.
Self-consolidating concrete (SCC) is a type of concrete that flows under its weight when it is fresh. It is used in sections with dense reinforcements or where mechanical vibration is impossible. By eliminating the need for mechanical vibration, self-consolidation concrete reduces the risk of segregation, bleeding, and other defects while increasing overall density and eliminating voids. Because of these characteristics, SCC is suitable for the majority of civil engineering structures.
Quarry dust and steel mill scale are two such waste products produced by aggregate crushing and steel manufacturing processes. Because of their fine particle size, these waste products may cause air pollution and water pollution if they end up in bodies of water. They may also cause sedimentation in hydraulic structures, raising the cost of repairs and maintenance.
Socio-Economic Benefits:
These quarry dust and steel mill scale, industrial waste products, must be used in the construction industry to achieve sustainability. It will not only reduce their environmental impact but will also relieve already overstressed natural resources. It will also reduce air and water pollution. Moreover, using waste products as a replacement for natural resources will result in a reduction in the cost of concrete per m3.
Project Objectives:
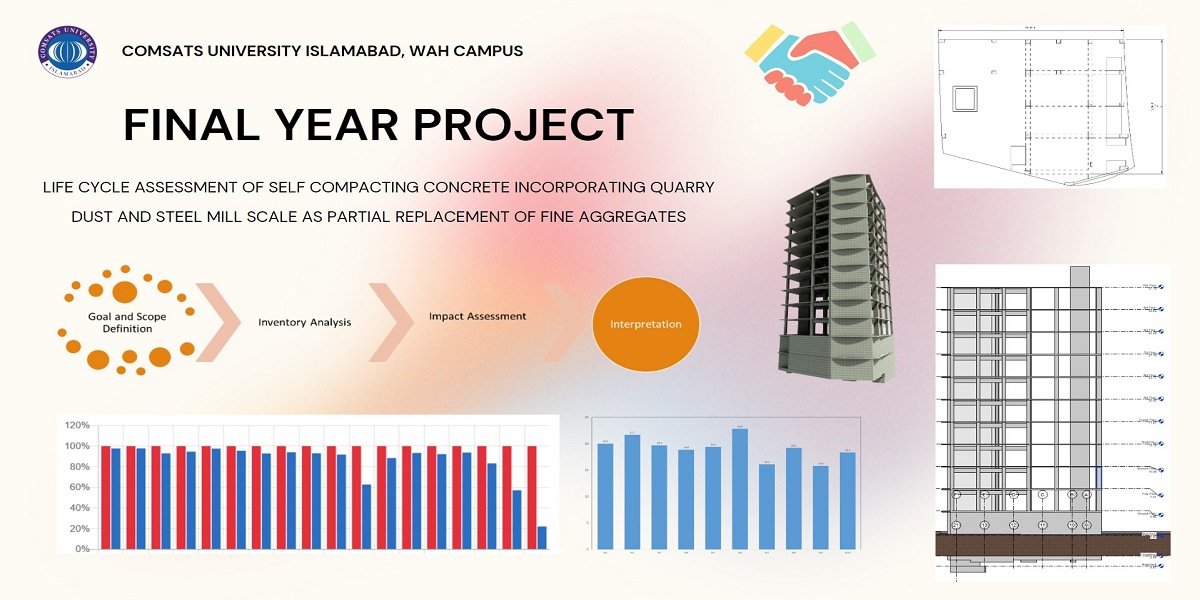
The purpose of this research is to determine the effects of incorporating quarry dust and steel mill scale as a replacement for natural sand in self-consolidating concrete and to carry out a life cycle assessment study to quantify the environmental impact of the optimized concrete and compare it with the environmental impact of control mix.
Methodology:
This research included the testing of concrete specimens for strength and durability. Concrete cylinders 4 inches in diameter and 8 inches in height were created to test these properties. These cylinders were then subjected to strength and durability tests as per ACI standards. These tests' results were optimized using design expert software, which employs the design of experiment (DOE) technique. Furthermore, the life cycle assessment study was carried out to determine the environmental impact of optimized concrete. A 10-story building was selected for the life cycle assessment study. The quantity takeoff of concrete for the life cycle assessment was computed by modeling the building using Autodesk Revit software, which employs building information modeling.
Outcome:
The compressive, splitting tensile, and flexural strength was increased up to 14, 16, and 50% as compared to the control mix. The life cycle assessment study revealed that the optimized concrete had an 80% reduction in water depletion, a 40% decrease in the urban land occupation, a 10% reduction in ozone depletion, a 40% reduction in natural land transformation, and a 2% decrease in specimen concrete (M5) were noticed as compared to the control mix. Hence it can be concluded that incorporating quarry dust and steel mill scale in self-compacting concrete will not only enhance the compressive, splitting tensile and flexural strengths of concrete, but will also prove to be very beneficial for the environment.