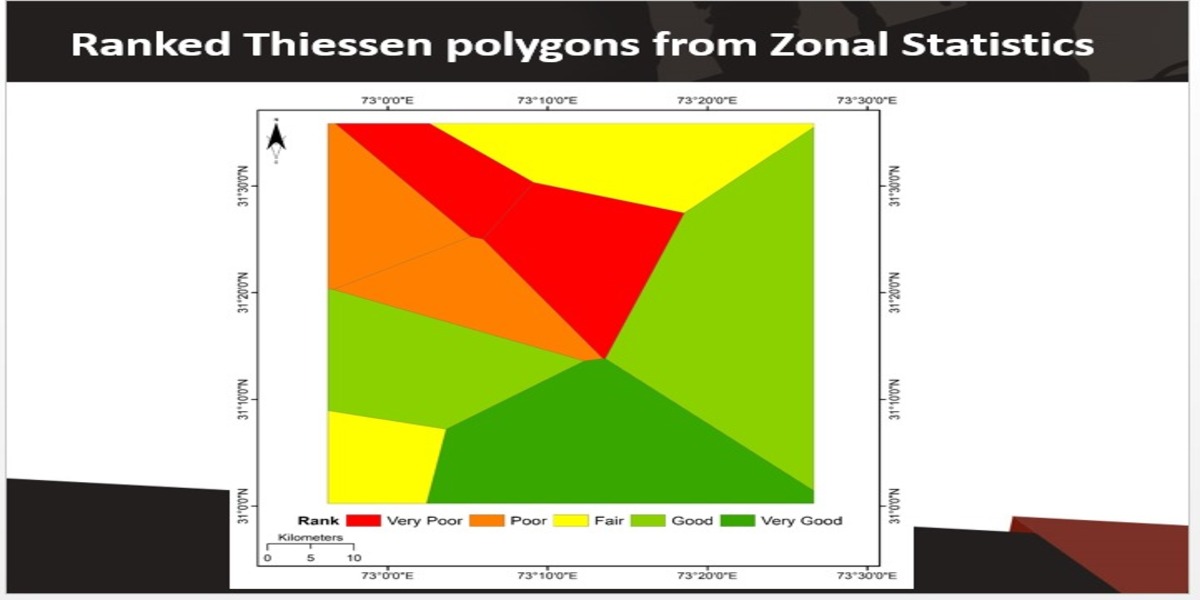
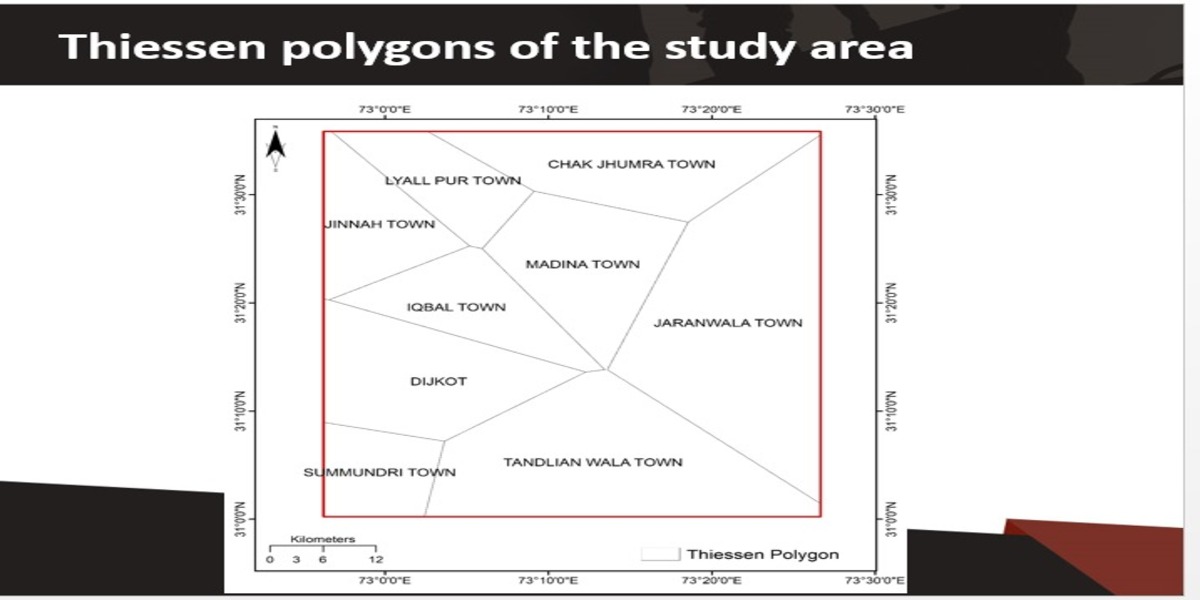
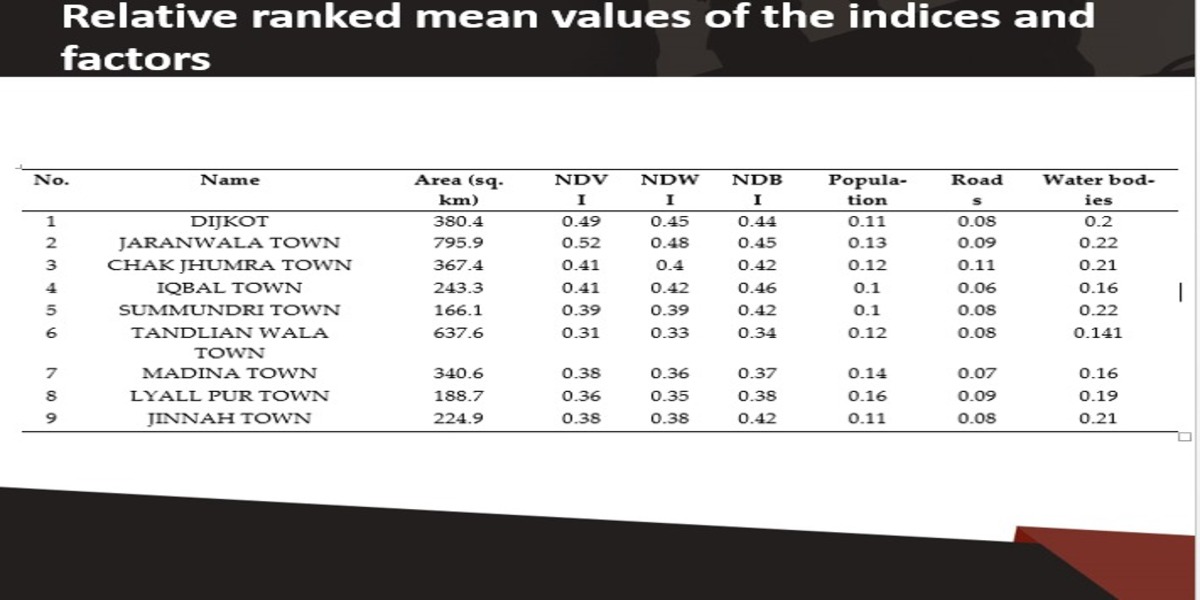
Disposal of municipal solid waste (MSW) is one of the significant global issues that is more evident in developing nations. Faisalabad is one of the largest industrial cities in Pakistan. It has many sustainability challenges and planning problems, including MSW management. The landfill sites were identified using remote sensing (RS) and geographic information system (GIS). The target area was distributed into 9 Thiessen polygons and ranked based on their favorability for the development and expansion of landfill sites. 70% of the area was favorable for developing and expanding landfill sites, whereas 30% was deemed unsuitable. The current study provides a reliable integrated mechanism based on GIS and RS that can be implemented in similar study areas and expanded to other developing countries.
- Objective:
- The potential influencing factors of site selection for construction waste landfills are identified based on the literature review. Then, an expert scoring process is employed, and the weight of each influencing factor is determined by the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and entropy method. Furthermore, the geographic information system (GIS) technique is used for spatial data screening and calculation. Finally, an evaluation framework for site selection of construction waste landfills is established. This model can be used to analyze the impacts of environmental as well as social and economic factors on site selection of construction waste landfills.
- Socio-economic Benefits:
- The current study has both practical and research implications. Practically, town, city, and regional planners, city governance teams, environmentalists, and policymakers can use the method proposed in this study to mark landfill sites and reduce environmental concerns.
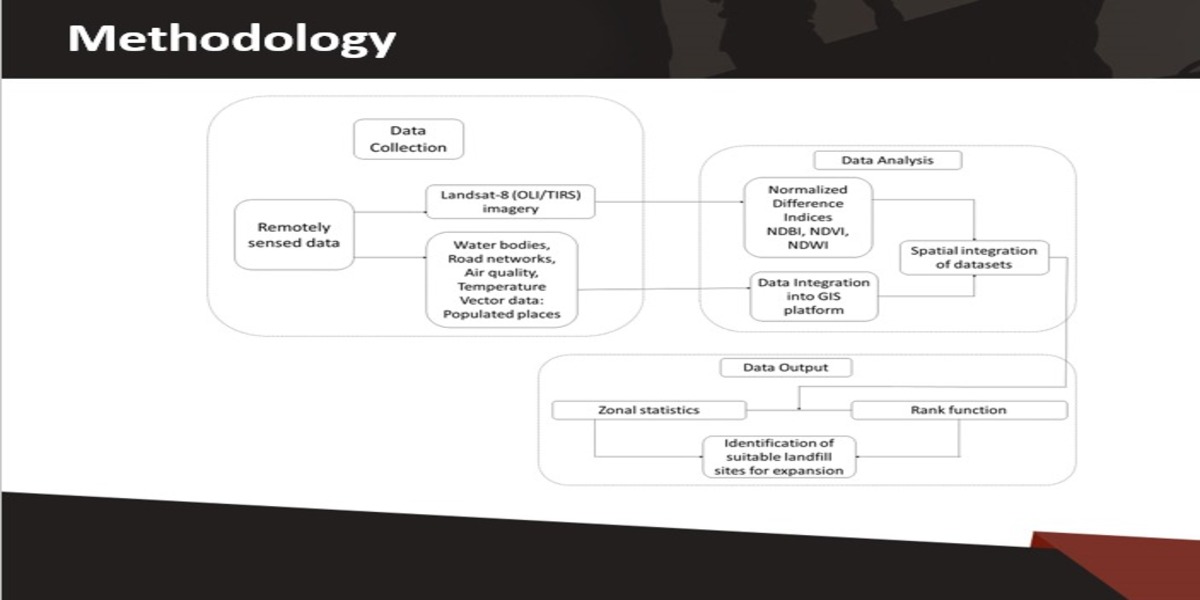
Project Methodology:
The methodology is based upon vector data and RS rather than opinions from experts for the ranking of parameters. The resulting categories have been proposed based on landfill site suitability. Technology (GIS-RIS) suggested rankings have been used in this study instead of expert opinion, where the flat surfaces have been represented by Thiessen polygons. This flexible approach provides a competitive edge for pre-or post-decision making in areas where expert advice is not accessible. the three key steps include data collection, analysis, and output generation. In data collection, remotely sensed data from Landsat-8 (OLI + TRIS) was downloaded. It consisted of water bodies, roads, air quality, temperature, vegetation, population, and other details. https://www.mdpi.com/2075-5309/12/5/605
Project Outcome:
Overall, the current study uses a combination of RS and vector data to locate and assess the best and worst landfill sites.And they are ranked among favorable areas for landfill. The current study has both practical and research implications. Practically, town, city, and regional planners, city governance teams, environmentalists, and policymakers can use the method proposed in this study to mark landfill sites and reduce environmental concerns.